There’s a reason environmentally-friendly initiatives and plans continue to dominate the headlines and our minds. Earth Day, after all, celebrates the promise of a more sustainable future.
What’s truly remarkable is just how much we’ve accomplished in the last few years just by the amount of information we have, alone, about this subject.
Then again, information is not everything we need. We have to improve our dependence on non-renewable energy with effort and focus.
If you’re looking for some basic background about renewable energy vs non-renewable energy, this article is for you.
Keep reading!
Renewable Energy vs Non-Renewable Energy
The difference between renewable and non-renewable energy is one of the most important concepts we need to understand in the 21st century. After all, we are at a time when concerns about our planet’s health are at their peak.
Fortunately, seeing the differences between these two forms of energy is easy just by defining each of them and providing examples of the different types they come in.
Renewable Energy
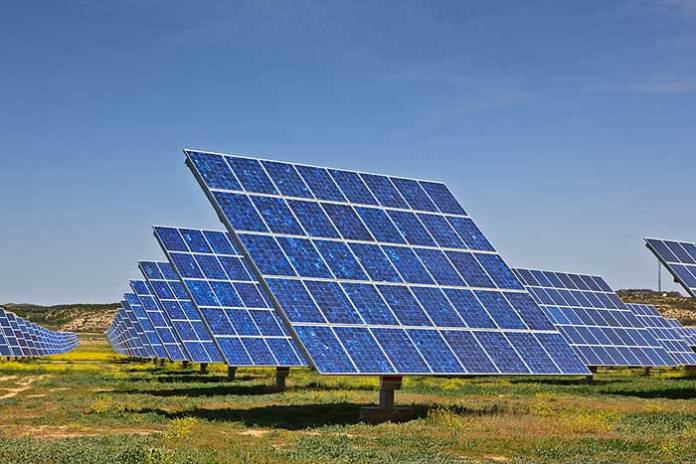
So, what is renewable energy? Put simply, it is an energy source that can be replenished or replaced naturally. Renewable energy comes in many different types, including solar, water, and wind energy. These are generated from the power of the sun, water, or wind to generate electricity.
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, while hydroelectric dams harness the power of moving water to generate electricity. Wind turbines use the wind to turn a generator and create electricity.
Biomass, another renewable energy source, uses organic materials, such as wood, to generate electricity.
Other renewable sources of energy that are less common but equally powerful are tidal energy, ocean waves and currents, ocean temperature shifts, falling water, and the earth’s heat (geothermal energy).
Non-Renewable Energy
As you can tell, non-renewable energy is the total opposite of renewable. It is obtained from sources that eventually run out, such as fossil fuels, which are created by heating and compressing organic matter under the earth’s surface.
Found in between layers of the earth’s crust, crude oil is another type of non-renewable resource and is the only one extracted as a liquid.
Another type of non-renewable energy derived from under the earth’s crust is natural gas, which usually consists of methane, propane, ethane, and butane.
Coal, which contains carbon and hydrocarbon matter, is yet another example and is made by compressing organic matter.
Other relatively uncommon forms of non-renewable energy include earth minerals, groundwater, land surface or soil, plastic, and nuclear energy.
Lesser Known Differences
We know the common differences between renewable and non-renewable energy, but there are two that are rarely discussed, yet also important – cost and requirements.
Here are the details:
Cost
The upfront cost of renewable energy is higher. However, the long-term savings will be well worth the initial investment. For example, it takes more money to generate electricity with solar panels than with fossil fuels. However, it’s cheaper to use solar energy in the long term.
Nonetheless, you can find companies that are willing to help you make your shift to renewable energy possible. For example, you can go solar with Blue Raven.
Infrastructure and Area Requirements
The infrastructure needed to collect renewable energy is more elaborate and less accessible in most countries compared to non-renewable energy.
Similarly, harvesting solar energy also calls for bigger land or offshore areas compared to non-renewable energy.
Most Concerning Differences
There is perhaps no other more alarming difference between renewable and non-renewable energy than the impact each makes on the environment.
Renewable energy is clean energy. That means its use is highly efficient and does not harm the environment. Non-renewable energy, on the other hand, is notorious for the following:
Greenhouse Emissions
The use of non-renewable energy leaves carbon dioxide and methane deposits in the air. Both add to climate change by trapping heat. Some of the effects of this phenomenon include extreme weather, wildfires, and problems with food supply.
Air Pollution
Non-renewable energy also emits different pollutants that can affect the environment and people’s health. In fact, non-renewables have been linked to early death, respiratory disorder, stroke, and even Alzheimer’s disease.
Acid Rain
Acid rain is produced when sulfur and other chemicals end up in the air in the process of harnessing non-renewable energy. The rain literally turns acidic, making it corrosive to machinery and harmful to local ecosystems, especially in lakes and streams.
Our Impact on Energy Sources as Humans
The whole world depends on these non-renewables for daily use. That is why these resources are going to run out.
This is also why we need to work more on developing renewable sources as more sustainable options. We must realize that we can always choose the type of resources we use for energy.
The more people use renewables, the higher their demand will be. Hence, the more we can make these energy sources more mainstream.
Making Educated Energy Choices
We need to be smart about the energy we use, which includes thinking about the future and not just the present. This begins with understanding the differences between renewable energy and non-renewable energy.
While non-renewable sources seem easier to come by, we need to stop thinking only about ourselves. We have to consider the generations after us, knowing that one tiny action we make can have a tremendous impact on their lives.
Want to read more engaging, enlightening articles like this renewable energy guide? Explore our blog!